Being an educator is the most rewarding and compelling thing for a human being. Encouraging a person’s learning and development is a complex task that requires attention to a number of complex challenges (the learner’s needs and interests, knowledge of the subject, the deeper meaning and impact of knowledge, and the practical application of difficulties in student life). As teachers, trainers, coaches, leaders, and parents; we often find ourselves facing these educational challenges.
The Kolb Educator Role Profile (KERP) provides a framework for assessing our preferred approach to educating others and maximizing our effectiveness in helping others learn and develop. It is based on a holistic typology of educator roles derived from Experiential Learning Theory.
Teaching around the learning cycle and different learning styles brings with it the need to rearrange the role that the person holds against students. Educational Role Profile (Kolb & Kolb, 2011) was created to help trainers understand the preferred teaching role and plan how they can adapt to a teaching around the learning cycle. Educational Role Profiles emerge as a combination of teaching role preferences, beliefs about teaching and learning, goals of the educational process, preferred teaching style and educational practices. Their educational role is not limited to individuals who are involved in formal classroom teaching.
This framework; It can be used for all individuals who have a teaching role at every stage of life, such as leader, coach, parent, friend.
The teaching role is a set of planned behaviors in response to the learning environment, including students and learning demands. Each teaching role encourages students to learn in an unparalleled way using an experience and a way of changing experience. In the role of facilitator, Trainers use concrete experience and reflective observation to help students get in touch and reflect on their own experiences. Subject experts use reflective observation and abstract conceptualization methods to help students connect the reflection and link it to the knowledge base. Students can provide models or theories to be used in later analysis. The standard determinant and evaluator role uses abstract conceptualization and active practice to help students apply knowledge to performance goals. In this role, trainers provide regular feedback by closely monitoring student performance according to the standards they set. Finally, the trainers, who adopt the coaching role, use concrete experience and active practice to mobilize students individually towards meaningful goals. These roles can be expressed in the face of the student in the form of knowledge centers across the application.
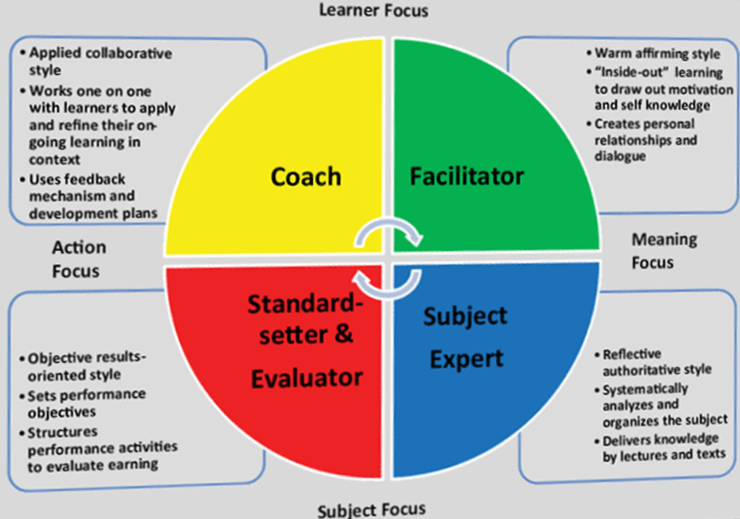
Educational Role Profile (ERP); Four roles are defined as facilitator, expert, assessor and coach. Trainers adopt these roles to help students maximize their learning capacity by passing through four stages of experiential learning.
Facilitator Role: In the role of facilitator, trainers help students connect and reflect on their personal experiences. Students adopt an intimate and positive style to reveal their interests, intrinsic motivation and knowledge about themselves. They often do this by encouraging small groups of dialogues. They establish personal relationships with students.
Subject Expert Role: In the role of subject matter expert, the trainers help students to connect the reflections of a subject to students in the knowledge base. They adopt authoritarian and reflective style. While systematically organizing and analyzing information on the subject, they often teach by examples, modeling and encouraging critical thinking. This information is often transmitted through lectures and written texts.
Standard Setter & Evaluator Role: As a standard determinant and evaluator, trainers help students master the knowledge and skills to meet their performance requirements. They adopt a result-oriented and objective style that determines the information requirements required for qualified performance. Students create performance exercises to evaluate their own learning processes.
Coach Role: Teachers who adopt the coaching role teach students to use knowledge to achieve their goals. In order to help them learn from their own experiences of life, they often work with individuals individually and adopt a collaborative, encouraging style. They help to create personal development plans and provide feedback on performance.
Most of us adopt each of these roles to a certain extent in education and training activities. One of the reasons for this is that these roles arise from our efforts to solve the basic dilemmas of the education process. Are we focusing on the experience and interests of the students or the requirements of the subject? Are we focusing on effective performance and practice or a deep understanding of the meaning of ideas? All necessary for effective learning at the highest level. However, individuals tend to prefer one or two roles to others because of the educational environment, such as educational philosophy, personal teaching style, administrative requirements, and student needs. Educational Role Profile is designed to increase your awareness of these preferences and to help you determine which of the most beneficial choices you have in your situation.